Zoo License Manager
Introduction
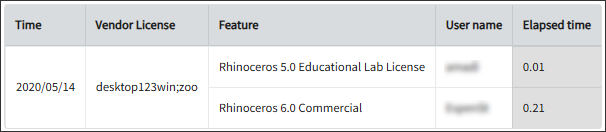
Open iT supports Zoo usage reporting by collecting log files and converting them to Open iT format.
An Open iT Core Client is installed on your license server for this collection. The data collector monitors and gathers the license usage history logs from the license manager every 5 minutes. Once the logs are collected, the data collection process triggers and the logs are passed to the data preprocessor. After the data is preprocessed, it is transferred to the Core Server for further storage, completing the history logs collection and processing.
Requirements
- An Open iT Core Client connected to an Open iT Core Server or a coexistent Open iT Core setup
- License server administrative rights
- Full path to the Zoo log files
Configuring Log File Collection
These are the required steps to configure the collection of Zoo log files.
- Windows
- Unix
-
Go to the Components directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\Configuration\Components, and back up thelogfilecollector-zoo.xmlfile. -
Open a command prompt with Administrator privileges.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin -
Once in the directory, set the location of the Zoo log files, run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_confinit -c "logfilecollector-zoo.xml.logfilecollector.source.dir=<zoo_log_dir>"where
<zoo_log_dir>is the location of the Zoo log files.Exampleopenit_confinit -c "logfilecollector-zoo.logfilecollector.source.dir=C:\ProgramData\Zoo"
-
Update the configuration file, run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_confbuilder --clientMake sure no errors are encountered.
Advanced Configuration
Refer to the Zoo Log File Collection Configuration table to learn more about Zoo configuration in logfilecollector-zoo.xml.
| Object Name | Accepted Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| source.dir | DirName (e.g., C:\ProgramData\Zoo) | Location of the Zoo log files. |
| source.pattern | String (i.e., *.log) | The glob pattern identifying source files in the source directory. |
| source.seen | String (collect, ignore, or tail) | Seen files are the previously collected source files.
|
| source.cmplines | Integer (e.g., 6, 10, 20) | This is required if the value of source.seen is tail. This is the number of lines compared to source files collected before to determine where to start the collection.Note: If this number is too low, you can end up with an incorrect position, and duplicate data may be in the log files. Usually, it is better to have a few lines more than strictly necessary than even a single line too little. |
| target.dir | DirName (i.e., ${OpeniT.directories.bin}/LogFileCollector) | This is the location of the directory containing the collected log data. |
| target.module | String (i.e., license) | The target type of module (in general). |
| target.datatype | String (i.e., zoo) | The specific type of target data. |
| target.interval | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1D) | The span of time between collector runs. |
| target.rotation-size | Integer (e.g., 6, 10, 20) | The log file rotates if it goes beyond the number (in mb) defined. |
| target.rotation-glob | String (e.g., *) | The glob pattern to match before the log file rotates. |
-
Go to the Components directory, which is by default in
/var/opt/openit/etc/Components, and back up thelogfilecollector-zoo.xmlfile. -
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
/opt/openit/bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd /opt/openit/bin -
Once in the directory, set the location of the Zoo log files, run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_confinit -r /var/opt/openit/ -d /var/opt/openit/etc/ -c "logfilecollector-zoo.logfilecollector.source.dir=<zoo_log_dir>"where
<zoo_log_dir>is the location of the Zoo log files.Example./openit_confinit -r /var/opt/openit/ -d /var/opt/openit/etc/ -c "logfilecollector-zoo.logfilecollector.source.dir=/root/zoo/logs"
-
Update the configuration file, run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_confbuilder --clientMake sure no errors are encountered.
Advanced Configuration
Refer to the Zoo Log File Collection Configuration table to learn more about Zoo configuration in logfilecollector-zoo.xml.
| Object Name | Accepted Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| source.dir | DirName (e.g., /root/zoo/logs) | Location of the Zoo log files. |
| source.pattern | String (i.e., *.log) | The glob pattern identifying source files in the source directory. |
| source.seen | String (collect, ignore, or tail) | Seen files are the previously collected source files.
|
| source.cmplines | Integer (e.g., 6, 10, 20) | This is required if the value of source.seen is tail. This is the number of lines compared to source files collected before to determine where to start the collection.Note: If this number is too low, you can end up with an incorrect position, and duplicate data may be in the log files. Usually, it is better to have a few lines more than strictly necessary than even a single line too little. |
| target.dir | DirName (i.e., ${OpeniT.directories.temp}/LogFileCollector) | This is the directory location containing the collected log data. |
| target.module | String (i.e., license) | The target type of module (in general). |
| target.datatype | String (i.e., zoo) | The specific type of target data. |
| target.interval | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1D) | The span of time between collector runs. |
| target.rotation-size | Integer (e.g., 6, 10, 20) | The log file rotates if it goes beyond the number (in mb) defined. |
| target.rotation-glob | String (e.g., *) | The glob pattern to match before the log file rotates. |
Zoo Events Log File Collection Configuration
This will produce the following aggregated data types used for historical reporting:
Activating Event Log Data Collection
These are the required steps to activate collection of event log data.
- Windows
- Unix
-
Open a command prompt with Administrator level privileges.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin -
Once in the directory, activate the collection of Zoo event log data, run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_oconfinit -u "collect_license_zoo_event-logs.root.scheduler.jobs.collect_zoo_licenselogs-events.general.active=true"
Open iT uses the openit_logparsergeneric binary to perform Zoo log parsing.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
/opt/openit/bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd /opt/openit/bin -
Once in the directory, activate the collection of Zoo event log data, run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_oconfinit -u "collect_license_zoo_event-logs.root.scheduler.jobs.collect_zoo_licenselogs-events.general.active=true"
Open iT uses the openit_logparsergeneric binary to perform Zoo log parsing.
Advanced Configuration
The collection runs every midnight by default. To configure the intervals, locate the instances attribute under collect_zoo_licenselogs, preprocess_zoo_licenselogs-events, preprocess_zoo_licenselogs-records, or transfer_zoo_licenselogs in the same file and configure the attributes.
Refer to the Zoo Log Job Scheduler Instances Configuration table to learn the attributes used to configure Zoo data collection and transfer.
| Attribute Name | Accepted Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max-instances | Uint (e.g., 5, 8, 9) | The number of instances allowed to run at the same time. |
| max-handling | String (end-oldest, end-all-old, or end-new) | The action done upon reaching the maximum number of instances:
|
| end-timeout | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1H) | The maximum waiting time before terminating a running instance. |
| quarantine | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1H) | The waiting time before starting a new instance after a previous one. |
Verifying Event Log Data Collection
After configuration, you can verify that the data is collected and sent to the Core Server by following these steps:
- Windows
- Unix
-
Open a command prompt with Administrator level privileges.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin -
Run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_executor -r collect_license_zoo_event-logs -
Verify that there are
archiver*.infiles created in the Core Server's archiver directory, which is by default inC:\ProgramData\OpeniT\Data\incoming\archiver.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
/opt/openit/bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd /opt/openit/bin -
Run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_executor -r collect_license_zoo_event-logs -
Verify that there are
archiver*.infiles created in the incoming directory in your defined data_dir($ROOT_DATA_DIR)upon Open iT Core Server installation.
Zoo Records Log File Collection Configuration
This will produce the following aggregated data types used for historical reporting:
- (89) Total License Use Licenseevents
- (90) Individual License Use Licenseevents
- (91) Usergroup License Use Licenseevents
- (108) Host License Use Licenseevents
- (109) Hostgroup License Use Licenseevents
Activating Record Log Data Collection
These are the required steps to activate record log data collection.
- Windows
- Unix
-
Open a command prompt with Administrator level privileges.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin -
Once in the directory, activate the collection of Zoo record log data, run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_oconfinit -u "collect_license_zoo_record-logs.root.scheduler.jobs.collect_zoo_licenselogs-records.general.active=true"
Open iT uses the openit_logparsergeneric binary to perform Zoo log parsing.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
/opt/openit/bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd /opt/openit/bin -
Once in the directory, activate the collection of Zoo record log data, run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_oconfinit -u "collect_license_zoo_record-logs.root.scheduler.jobs.collect_zoo_licenselogs-records.general.active=true"
Open iT uses the openit_logparsergeneric binary to perform Zoo log parsing.
Advanced Configuration
The collection runs every midnight by default. To configure the intervals, locate the instances attribute under collect_zoo_licenselogs, preprocess_zoo_licenselogs-events, preprocess_zoo_licenselogs-records, or transfer_zoo_licenselogs in the same file and configure the attributes.
Refer to the Zoo Log Job Scheduler Instances Configuration table to learn the attributes used to configure Zoo data collection and transfer.
| Attribute Name | Accepted Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max-instances | Uint (e.g., 5, 8, 9) | The number of instances allowed to run at the same time. |
| max-handling | String (end-oldest, end-all-old, or end-new) | The action done upon reaching the maximum number of instances:
|
| end-timeout | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1H) | The maximum waiting time before terminating a running instance. |
| quarantine | Timespan (e.g., P30S, P5M, P1H) | The waiting time before starting a new instance after a previous one. |
Verifying Record Log Data Collection
After configuration, you can verify that the data is collected and sent to the Core Server by following these steps:
- Windows
- Unix
-
Open a command prompt with Administrator level privileges.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd C:\Program Files\OpeniT\Core\bin -
Run the command:
Command Syntaxopenit_executor -r collect_license_zoo_record-logs -
Verify that there are
archiver*.infiles created in the Core Server's archiver directory, which is by default inC:\ProgramData\OpeniT\Data\incoming\archiver.
-
Go to the bin directory, which is by default in
/opt/openit/bin, run the command:Command Syntaxcd <bin_dir>Examplecd /opt/openit/bin -
Run the command:
Command Syntax./openit_executor -r collect_license_zoo_record-logs -
Verify that there are
archiver*.infiles created in the incoming directory in your defined data_dir($ROOT_DATA_DIR)upon Open iT Core Server installation.
Sample Reports
Max Available vs Max in Use
This sample report compares max in-use licenses against max available licenses.
It offers several key benefits:
- Optimized License Allocation – helps ensure you are not over-purchasing licenses you don't need or under-provisioning.
- Cost Savings – identifies opportunities to downgrade or redistribute licenses, reducing unnecessary expenses.
- Usage Trends & Capacity Planning – shows peak usage patterns, allowing better forecasting for future needs.
- Avoiding Service Disruptions – helps prevent situations where users cannot access software due to reaching the license limit.
- Compliance & Audit Readiness – provides a usage record to ensure compliance with vendor agreements and avoid penalties.
- Performance & Productivity Insights – helps assess whether certain teams or departments are under-utilizing or over-utilizing software.
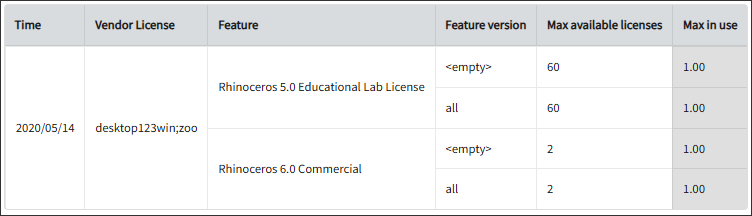
Feature Elapsed Time per User
This sample report gives you helpful insights into software use, performance trends, and user behavior.
It offers several key benefits:
- User Efficiency Analysis – tracks how much time users spend on specific features to help assess productivity.
- Identifying Workflow Issues – highlights any delays or inefficiencies in processes that could be improved.
- Usability & UX Insights – points out features that take longer to use, which could indicate design or functionality improvements.
- Training & Support Guidance – helps identify users who might need extra training to use a feature more effectively.
- Compliance Tracking – makes sure users are spending the right amount of time on regulated tasks.
- Resource & License Optimization – finds underused features or areas where too much time is spent, helping with better resource allocation.